|
Consulting
An Overview Seminar to
Indiana University MBA Students
Eugene B. Lieb
Custom Decision Support, Inc.
http://www.lieb.com
ã Copyright Custom Decision Support, Inc. (2001)
September 2001 |
|
Agenda
The Nature of Consulting
Types of Consulting Services
Using Consultants
So You Want to be an Independent Consultant
|
|
Consultancies
"Consultancies" is Vaguely Defined
Spectrum of Services Provided by Consultancies
Outsourced Services are well Defined Products (Contracts)
Advisory Service Often Go Along for the Ride
|
|
Traditional Outsourced Services
(Doing Things)
Advertising and Promotion Placement
Market Information and Marketing Research
Legal Services and Support
Information Systems Development and Support
Accounting Services
Training
Tool Manufacture
|
|
STRICTLY Advisory Services
(Finding out Whatís Wrong)
Financial Audits
- Independent Financial Statement Audits*
- Financial "Deal" Audit (New Businesses)
- Control Audits
Strategic Audits
- Portfolio Audits
- Forecast Audits
- Marketing Audits
Operational Audits and Certifications
- Quality Audits and Certification
- Manufacturing Reviews (Benchmarking)
- Process Audits
- Policy Audits
|
|
In-Between
(Finding Out What to Do)
Planning Support
Operational Development
Market Evaluation
Marketing Research
Meeting Facilitation
Advertising Creation
Forecasting Systems
Decision Support Systems Development
|
|
UNOFFICIAL Advisory Functions of an Independent Consultant (or Why Use One?)
An Outsiderís View
A Communications Conduit
- From the Troops to Management
- From Management to the Troops
- Saying the Unsaid
Asking the Unaskable Questions (Emperorís Clothes)
Based on the "Temporary" Assumption
|
|
Classic Advisory activities
Large Consulting Firms
Accenture, KPMG, BCG, Bain, McKensey & Co., etc.
Contracts: The Highest Level of Management
Customer Value:
- Compelling Directions for Action
- Due Diligence
|
|
Strategic Audits
Goal: To derive optimum directions through the analysis of operations and business conditions.
Based on Extensive Analysis of Internal Data
Supported by Interviews with Key Personnel
And Proprietary Market Information
Customer Value:
- Buy-in to Strategic Directions
- Excuse for Radical Reorganization
- Board Level Support
|
|
MIs Needs Audits
Goal: To propose an optimum Information Systems to obtain justifying competitive advantage
Preliminary for an Implementation Contract, (Loss Leader?)
Customer Value:
- Justification for a Large Investment
- Insight into Unknown Technology
- Experienced Advisors
|
|
Themes of the "Month"
Goals: To be Ahead of the Curve in the New Management Procedures
- Total Quality Management
- Management Orientation
- E-Business
Programs in Support of On-Going Clients
Customer Value:
- Improved Profitable Management Organization
- Meet Customers Expectations
- Provide a Halo of Management Competence
|
|
Traditional Complaints - Large Firms
The "Green Team" (Inexperienced Workers)
"Telling me what I already know"
Using Our Own Data
Excessively Expensive
Nothing New
Donít Stay Long Enough to Do Anything
|
|
Power and Influence
The Effect of the Consultant Acts through the Client
Large Firms Interface with Upper Senior Management
- Downward focused Authority
- Value is Credibility
Small Firms Interface on the Business Level
- Downward authority with in the Business Unit
- Only Influence Upward
|
|
Small Consultancies
Covers a Broad Range
- Single Practitioner supported by Technology
- Medium Size Specialty House (The Kotler Group, ARBOR, etc.)
Focus is on the Service Provided
Customer Value:
- Solution to a Problem
- Support (Advisory Services) Supplement
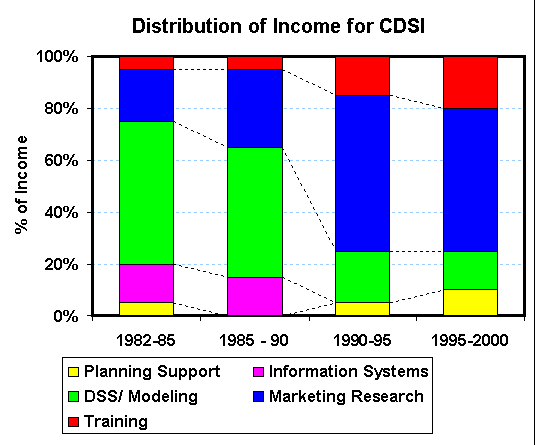
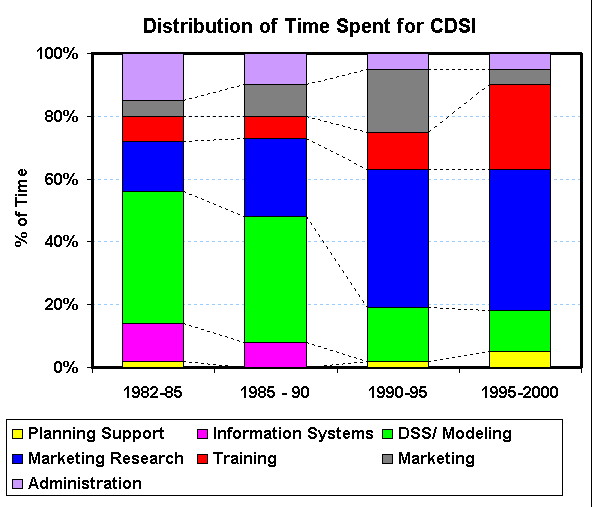
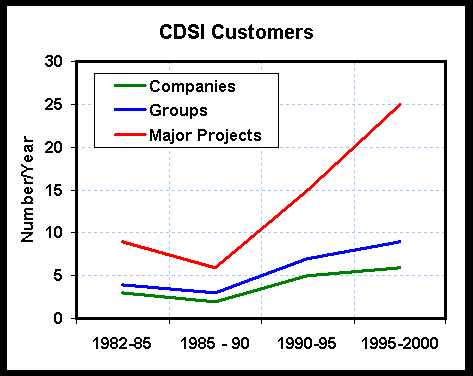
Example will be Custom Decision Support, Inc.
|
|
Business Planning Support
Goal: To assist in the Solution of a Specific Business Problem through the Development of a Written Business Plan
Do what needs to be done:
- Facilitation of Planning Meetings
- Analysis of Operations
- Writing of Drafts
Customer Value:
- Outsourced Management Resource
- Force to Resolve the Issue
- Outsiders View
|
|
Marketing Research
Goal: To Understand the Market and Provide Due Diligence
Activities:
- Problem Formulation
- Design, Execution, Data Analysis
- Interpretation
Customer Value:
- A Quantitative Basis for Decision Making
- Market Insight
- Management and Troop Support for Actions
|
|
Decision Support systems
Goal: To be on the Leading Edge of Management Science and Provide Due Diligence
Models Cover a Broad Range
- Pricing Models
- Expansion (Industry) Models
- Sales Aides
Customer Value:
- Answering Some of the What-If Questions
- Gaining Management Support
- Obtaining Group Buy-in
|
|
Being Successful as a Consultant
Independent or Internal
Saying No!
Listening
Working with the Organization
Recognizing Who has Power (Influence)
Being Willing to Walk Away
Matching Personalities and Skills
|
|
Cultures, Businesses, and Consultants
Firms divide between "Professional" and "Entrepreneurial"
- This is the traditional distinction between large and small
- However, it is not a question of size but culture
Professional Organization Understands Specialization and Use Consultants
Entrepreneurial Organizations Focus on "Generalists" and Use Suppliers as Consultants
Most Truly Large Firms Sub-divide into the Units that Correspond to Relative Small and Medium Size Operations
|
|
Reasonable Expectations of Clients
To be Competent in the Field of Expertise
To have the "Best Interests" of the Clientís Firm in Mind (Trust and Loyalty)
To be "Honest" and Relatively "Open" with Client
To be Tactful and Discreet within and outside of the Clientís Organization
To Complete Projects On-Time and within Budget
Follow "Corporate Guidelines" when associated with the Clientís Firm
|
|
Reasonable Expectations of Consultants
To be Paid in Full and On-Time
Not to "Have Your Chain" Pulled (Consulting for Free)
To be Informed on Project and Business Status as Soon as Possible
To Have Access to the Internal Communications
To be "Honest" and Relatively "Open" with the Consultant
|
|
Successfully Using Consultants
Call in Consultants Only When You Need Them
- Use Consultants Only for Their Expertise
Understand What You Expect from the Consultant
- Objectives, Goals, Real Deadlines, and Budgets
Clearly and Repeatedly Communicate that to the Consultant and Yourself
- Make the Consultant Reflect It Back
Do Not Expect the Consultants to Do Managementís Job
- They Should Not Make the Decisions
Meet Your Organizations Commitments on Time
Make Clear End Points of Projects
Require Good Documentation with Presentations
|
|
So You Want to be an Independent Consultant!
Tough Clients are Almost Always Easier to Handle than Tough Bosses
Your Time is Under Your Control:
- You Can Work Any 70 Hours a Week you Choose
- Rationality Never Governs Client Demands
Though Some Independent Consultants Make a Good Living:
- On Average Similar Level Managers Do at least as Well
- Some Tax Breaks, Some New Taxes
- High Uncertainty and Variation in Income
- No Paid Insurance or Retirement Fund
It is Very Learning Business and Usually Not Boring
- You Have to Do Everything!
- Need to Stay Flexible.
|
|
Being Successful as an Independent Consultant
All responsibilities are yours
Control your time (Peter Drucker "The Effective Executive")
As with all business: The Key is Marketing and Sales
- You Must Do It All the Time!
Know your weaknesses
- Be very honest with yourself
- Avoid situations which expose your weaknesses
- Use resources and partnerships to support your weaknesses
Build on Relationships (Pay attention)
Exploit your Strengths
|
|
Success of a Start-up Consultancy (New Business)
You Need a "Sugar Daddy"
- Large Quality Client
- Willing to Stay with You
- Willing to Support You for a Number Years
An Existing Market
- You Canít Build a Market "Gittlemanís Law"
- Provide Well Defined Existing Services
Give Exceptional Customer Value
- Faster (more Response) than the Competition
- Cheaper than the Competition
- Better than the Competition
Control Costs and Your Ego
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Observations on Consulting
Clients are Generally Unable to Differentiate Between Competence and Excellence
Clients are Hyper-sensitive to Responsiveness
Clients Always want more than they Say
Uninformed Troops are Always Suspicious of Consultants
Clients are less Price Sensitive than they appear
|
|
Summary
Consulting Covers a Wide Range of Services
The Customer Value focuses on Assistance and Advise
Clearly Defined Scope and Objectives is Critical for Successful Use of Consultants
Being an Independent Consultant is Rewarding but a Lot of Work
|